Because of the versatility of hydrogen, green hydrogen has the potential to fundamentally change the global economy and usher in a new era of economic prosperity, sustainability, and energy independence to those with access to solar, wind and water.
At the center of this extraordinary opportunity is a hydrogen generator that can produce cheap green hydrogen.
The applications for green hydrogen range from small to massive, including:
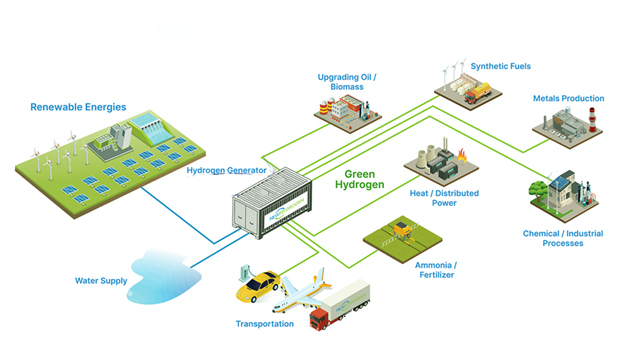
Unlike lithium-ion battery technology, which is simply a battery evolution, green hydrogen technology is revolutionary and can dramatically affect the global economy.
Hydrogen is increasingly considered as one of the most promising zero-emission technologies for future aircraft. Hydrogen can be used as fuel onboard an aircraft in three ways: as a source of power for battery-like fuel cells, in hybrid aircraft, or as combustible fuel. Hydrogen has an energy-density-per-unit mass that is three times higher than traditional jet fuel. One specific challenge is how to store hydrogen on board the aircraft. Today, liquid hydrogen storage is among the most promising options, while storing hydrogen as compressed gas poses challenges with current aircraft weight and volume requirements1
Hydrogen is used in oil refineries for many purposes. One of the most important uses is to remove sulfur from fuels produced in a chemical separation process called hydrodesulphurization. In this reaction, hydrogen bonds with sulfur to form hydrogen sulfide which is captured and further processed in another treatment step. Hydrogen also plays several key roles in a refinery. It is both used as a “catalyst” (to stimulate chemical reactions) and as a process byproduct that (in certain concentrations) can be an indicator that some critical action must be taken. Petroleum refineries use hydrogen in downstream units, such as hydrocrackers and hydrotreaters, to meet fuel specifications for producing distillate, jet fuel, and other petroleum products. Hydrogen is particularly important in processing low-grade, sour crude slates that are rich in sulfur content.
Hydrogen is used in industrial heating for many purposes. Hydrogen’s high thermal conductivity provides superior heat transfer to speed full-depth materials processing. Hydrogen may enable cycling parts more quickly – running the furnace faster – because of higher heating and cooling heat-transfer speed.
Hydrogen is used broadly in the pharmaceutical industry. It is used to manufacture vitamins and other pharmaceutical products. Hydrogenation has been widely embraced by the chemical and pharmaceutical industries since the 1960s. Large quantities of hydrogen are used to purify gases (e.g., argon) that contain trace amounts of oxygen, using catalytic combination of the oxygen and hydrogen followed by removal of the resulting water.
Hydrogen is used as the primary fuel to drive the ship in two primary ways: Method A – to use it directly in the internal combustion engine (i.e., in the engine of the ship) in place of the traditional fuel (MDO) or Method B – to use the hydrogen to run fuel-cells onboard which will in turn generate electricity to drive the vessel. Ships powered by green hydrogen could help meet the emissions reduction targets of the shipping industry.
Hydrogen is used in cars and trucks of the future as a fuel source for fuel cell vehicles. A hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle uses the same kind of electric motor to turn the wheels that a battery-electric car does. But it’s powered not by a large, heavy battery but by a fuel-cell stack in which pure hydrogen (H2) passes through a membrane to combine with oxygen (O2) from the air, producing the electricity that turns the wheels plus water vapor. Hydrogen trucks are gradually becoming a thing, and in a decade or so they are likely to seriously start replacing the diesel fleets.
Hydrogen is the key ingredient in making ammonia, which is in turn is a key ingredient in fertilizers. Without hydrogen, the world would not have fertilizers.
Electrolyzers are well suited and scalable for distributed onsite green hydrogen generation in fueling station applications. With green electricity from a nearby solar array or renewable electric grid, green hydrogen can be produced anywhere and anytime. This distributed model of hydrogen production eliminates the need for expensive transportation from a centralized facility.
Hydrogen has many industrial uses. It is used in the production of ammonia, methanol, and petroleum products. It is also used in the refining of metals and in the production of electronics.
Green hydrogen can help building heating by blending it into the existing distribution system. It will help to decarbonize the existing gas networks and is expected to heat approximately 800 homes, as well as providing pure and blended hydrogen for use in vehicles.
Hydrogen is used in the power industry for many purposes. Hydrogen can be used to power fuel cells or internal combustion engines. It can also be mixed with natural gas to reduce emissions or supply 100% of the heating fuel. Green hydrogen can provide on-demand dispatchable renewable electricity by combustion or fuel cells. It can power vehicles, appliances, and electronic devices.
Hydrogen is used in food processing to protect the nutritional and sensory properties of the product during the storage period or the preparation of the final product. Hydrogen gas has reducing capacity, antioxidant activity, and zero residual and eco-friendly properties which make it a multi-purpose candidate for various crop production and food processing.